| |
SELF-EMPLOYMENT
TAX BASICS
By, Peter Jason
Riley, Certified Public Accountant
We can see from
this diagram that income from self-employment is subject to two levels
of taxation:
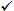 |
The first is the 15.3%
self-employment tax. This tax has 2 elements: 2.9% is Medicare tax and 12.40%
is Social Security taxes that the IRS collects on behalf of the
Administration. Social Security tax is only applied on the first $160,200 of income in 2023 ($168,600 in 2024). Medicare tax is calculated on all the self-employment income. It is important to remember that your personal exemptions and deductions for your home interest, real estate tax, and state taxes, etc. do not affect the calculation of this tax. |
 |
The second is, of course, federal income tax. IRS Guide to Employment Taxes |
Other issues to be considered:
- You will
be allowed to deduct 100% of your health insurance costs as a trade or business
expense.
- Your income will
not be subject to withholding tax. However, you will be required to
pay estimated taxes quarterly.
- You will have
to maintain complete records of your income and expenses. In particular,
you should pay attention to recording your expenses in order to be
able to take the full amount of the deductions to which you are entitled.
See our special tax deduction checklists for more information on possible
deductions you may be entitled to. Certain types of expenses, such
as automobile, travel, entertainment, meals, and home office expenses,
are subject to special recordkeeping requirements or limitations of
their deductibility and require special attention.
- If you hire any
employees, you will have to get a taxpayer identification number and
will have to withhold and pay over various payroll taxes.
- You should consider
establishing a qualified retirement plan. The advantage of a qualified
retirement plan is that amounts contributed to the plan are deductible
at the time of the contribution, and are not taken into income until
the amounts are withdrawn. Because of the complexities of ordinary
qualified retirement plans, you might consider a simplified employee
plan (SEP), which requires less paperwork or the SIMPLE
IRA's, or the SOLO 401K. If you do not establish a qualified retirement plan, you may
make a contribution to an IRA. IRS Guide to Retirement Plans
Remember, this
is a very simple outline of the basic tax
matters involved in self-employment income.
It is not meant to be the complete story!
© Copyright 2001-2026
Riley Business Services
978.270.9260
All Rights Reserved
Disclaimer
|
|





